In the Data Engineering Lifecycle, we typically focus on Extraction, Transformation, and Loading (ETL) or Extract, Load, and Transform (ELT). These traditional processes are designed to move raw data into a central repository, like a Data Warehouse, where it can be analysed.
However, the industry has seen the emergence of a newer process called Reverse ETL.
What is Reverse ETL?
Reverse ETL is exactly what it sounds like: it reverses the direction of the traditional data flow.
Instead of sending operational data into the data warehouse for analysis, Reverse ETL takes analytical, transformed data that resides in the Data Warehouse or Data Models and pushes it back into the source system, often different to its original source.
The Data Flow
Reverse ETL is considered one of the final outputs of the Data Engineering Lifecycle, categorised alongside Analytics and Machine Learning outputs during the Serving phase.
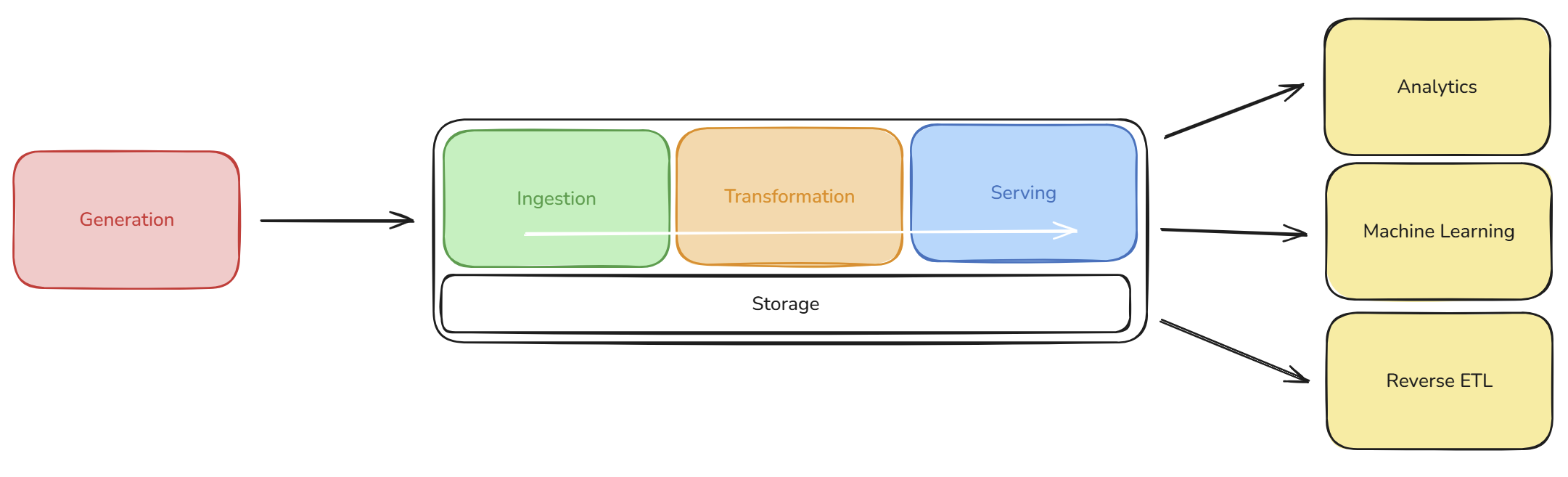
In a typical Reverse ETL workflow, data moves:
- From the Data Models (where metrics are calculated and refined).
- Back into the source system (e.g., SaaS applications, relational databases, or CRMs).
This process is recognised as part of the pipeline architecture in modern data platforms.
Why is it Necessary?
The main purpose of Reverse ETL is to make data analysis accessible to operational teams directly, where they perform their daily work, without having to use another reporting tool like Tableau or Power BI.
If a critical metric is only available in a Business Intelligence (BI) tool or an internal data model, it requires a business user to manually query or look up that insight. Reverse ETL eliminates this friction, ensuring that data is available where business users are already working.
A Practical Example
Consider a scenario where a company calculates the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) in their Data Warehouse.
To make this calculated value actionable for the sales team, the company can use Reverse ETL to feed the CLV back into a system like Salesforce. This allows sales representatives to instantly see the predictive value of a customer directly on the customer's profile in their CRM, without needing to open a separate analytics dashboard.
