Tableau Prep is a tool used to clean and reshape any data that is considered messy. This allows the data to then be ready for visual analysis through Tableau Desktop to communicate said data. Cleaning is beneficial as it is time efficient and removes any errors to produce the highest quality version of said data. Tableau Desktop does contain some similar features to Prep such as filtering and renaming fields. However, Tableau Prep is specifically designed for cleaning which provides more flexibility and control. It fills a gap in the process of cleaning messy data so it is ready for visual analysis.
Knowing your data and understanding what the desired state your data should be in is very important. Let's look at some important aspects:
- Field - a column which contains a data type (strings, integers, decimals, etc.)
- Record - a row containing a single instance of information
- Measure - quantitative data (e.g. height and weight)
- Category - qualitative data (eye and hair color)
- Granularity - how detailed your data set is
Granularity is important to understand so you can make more informed decisions based on your data. Knowing your data involves identifying measures and categories, null values, data types etc. An overall idea of how your data is structured can save a lot of time.
Onto inputs and outputs which may seem simple but there is much information to understand behind the scenes.
Inputs involve bringing data into Tableau Prep to be cleaned and reshaped whereas, outputs involve saving and extracting into different output types. Different file types such as; CSV, Excel files can be inputted into Tableau Prep and they can be found either on your computer or a server. Connectors allow data sources to connect to Tableau Prep, examples include; Amazon Redshift and Microsoft SQL server. One thing to note is that you can input files from Tableau Server. Let's look at how we actually input data.
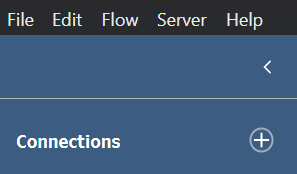
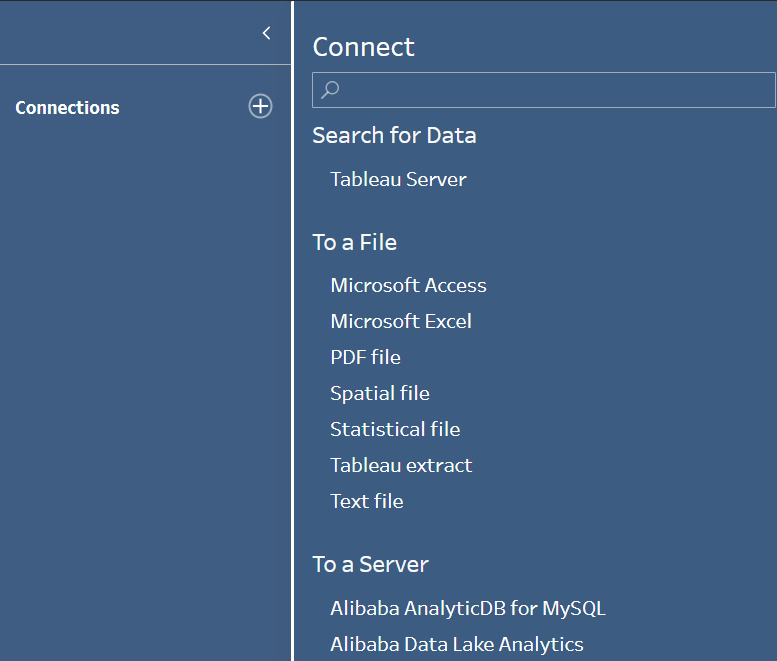
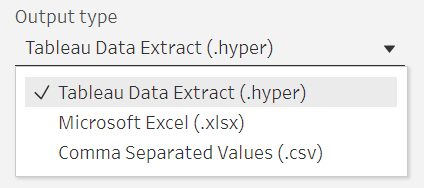
Outputs involve extracting the prepared data which involve for different output types - CSV, TDE, Hyper and a public server. TDE and Hyper file outputs are Tableau file formats and they both have their advantages and disadvantages. With Hyper being smaller but more optimized for extraction. Depending on where you want to save your file (to your computer or a server) the output type may change. Again, let's look at how we output files.
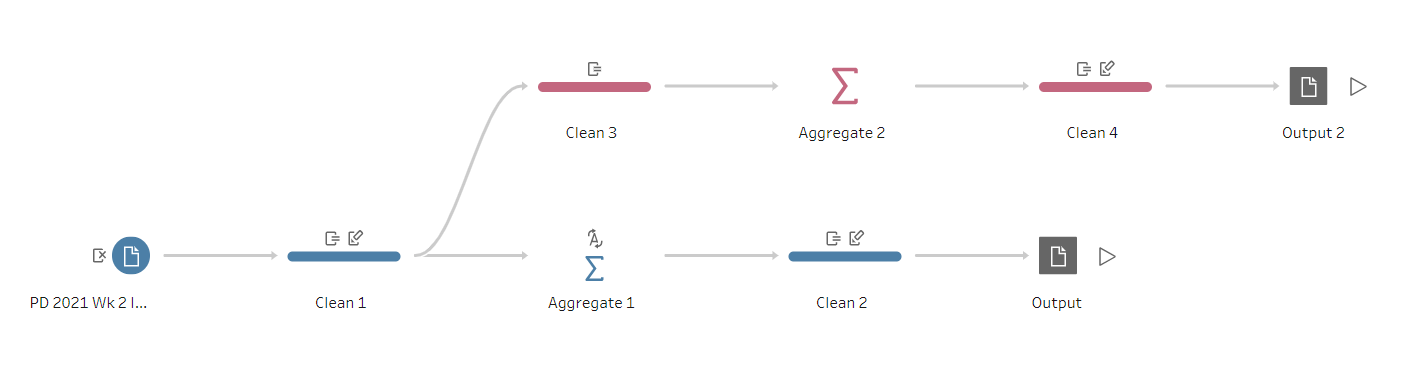
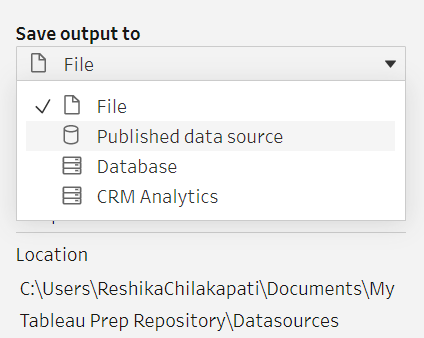
In summary:
- Cleaning data is important to make better informed decisions on your data
- Tableau Prep is specifically designed for this task
- Inputs involve bringing data into Tableau Prep
- Outputs involve saving the file and extracting the data
