How does a weighted average differ from a normal average?
The weighted average is the average found in a set of data that identifies specific numbers as having more weight or having more value than others. The weighted average is different from determining the normal average of a set of data as the total shows that some parts of the data account for a higher weight or proportion, meaning they're more significant than others or appear more often in the data. A normal average, on the other hand, assigns all numbers equal weighting. Using a weighted average gives a more precise observation of a set of data than using the normal average by itself.
How do you work out a normal average?
Normal Average = Sum of values in a range / number of values in a range
How do you work out a weighted average?
You calculate the weighted average by multiplying each value in the set by its weight, then you add up the products and divide the products' sum by the sum of all weights.
Weighted average = score1 * weight1 + score2 * weight2 + . . . + Score5 * weight5 / sum of all weights
Example
Let's calculate the normal average profit and weighted average profit using sample superstore data in Tableau.
To calculate the normal average profit we right click on the green pill for 'profit' > measure > average (see table below).
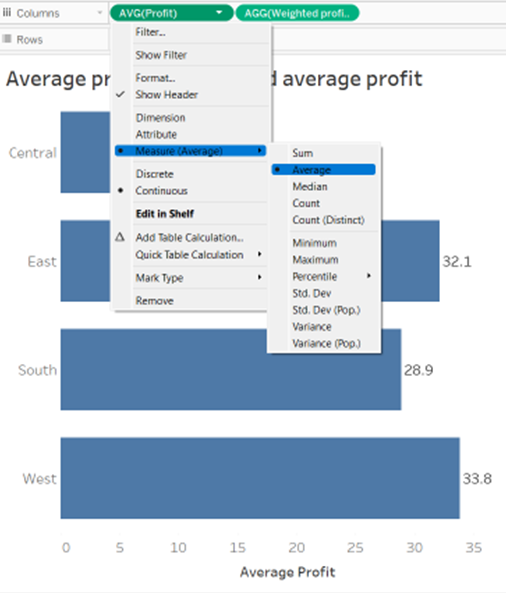
To calculate the weighted average profit we use the following calculation:
SUM([Profit]*[Quantity])/SUM([Quantity])
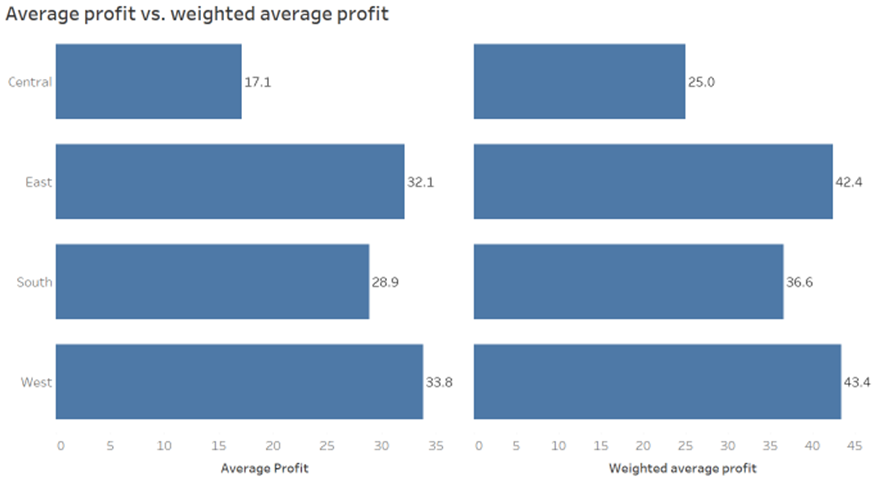
The table above shows the results of a normal average calculation and a weighted average calculation. We can see that using normal average and weighted average produces different results.
