Level of Detail calculations, often referred to as LOD is a type of calculation that allows you to perform aggregations at a different level of detail to what is in your view. To be able to understand how to perform LOD calculations, first you need to be able to differentiate between [Dimensions] and [Measures].
Dimension - qualitative/categorical data. It is able to breakup your view. An example of which is Sub-category in the Superstore dataset in Tableau.
Measure - numerical data, can be aggregated e.g., SUM([Sales])
There are 3 types of LODs, FIXED, EXCLUDE and INCLUDE and they all follow the same form:
{ TYPE OF LOD [Dimension(s)] : AGGREGATED([Measure])}
It is important to note that Dimension(s) is optional, the LOD will still work without the dimension there.
FIXED LOD
A FIXED LOD works independently to what is in the view, this means that no matter the number of dimensions you have on the rows/columns, the FIXED only responds to the expression written in the calculation.
Example:
Bellow we want to return the sum of sales per category without it being affected by the presence of Sub-category. As you can see the FIXED column only changes when the category changes.
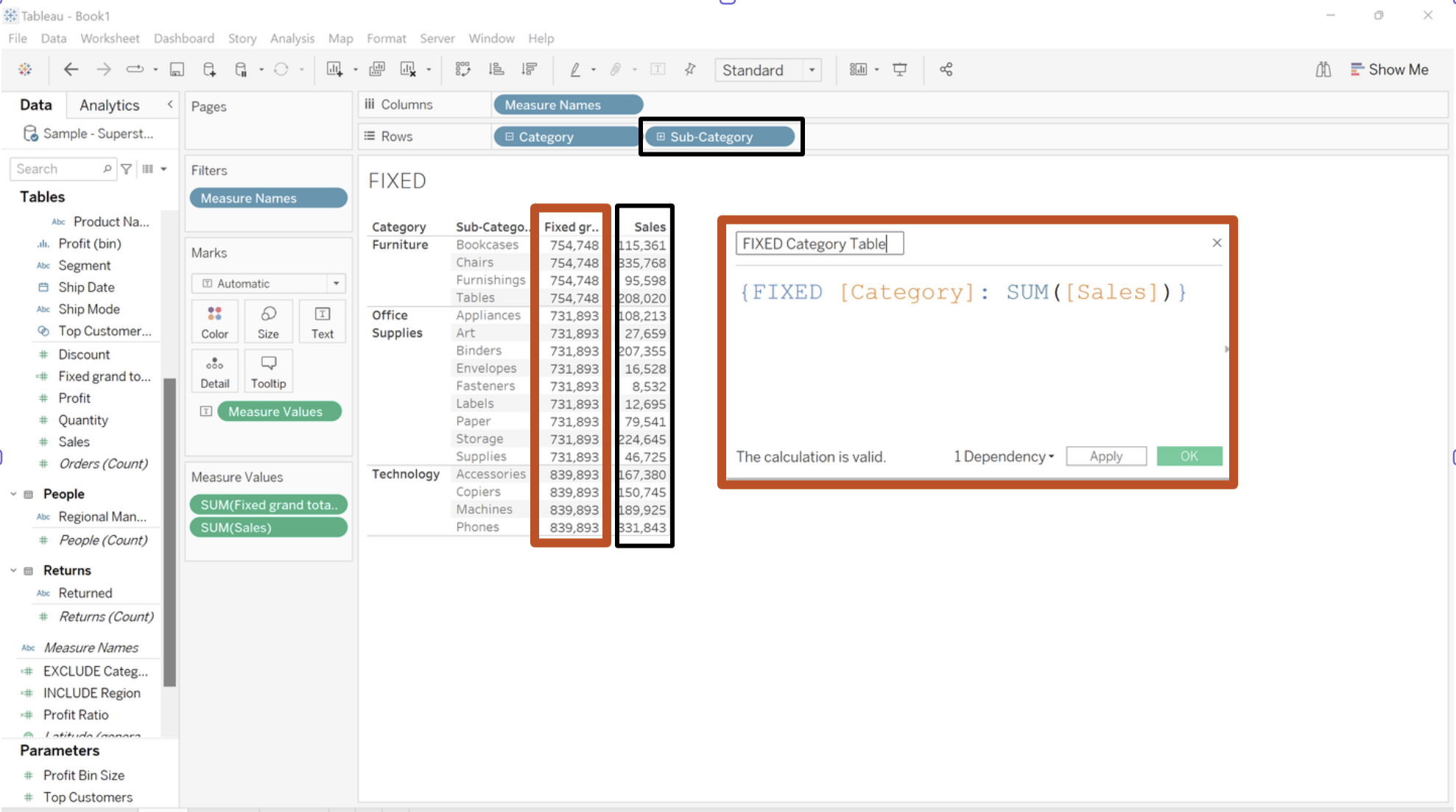
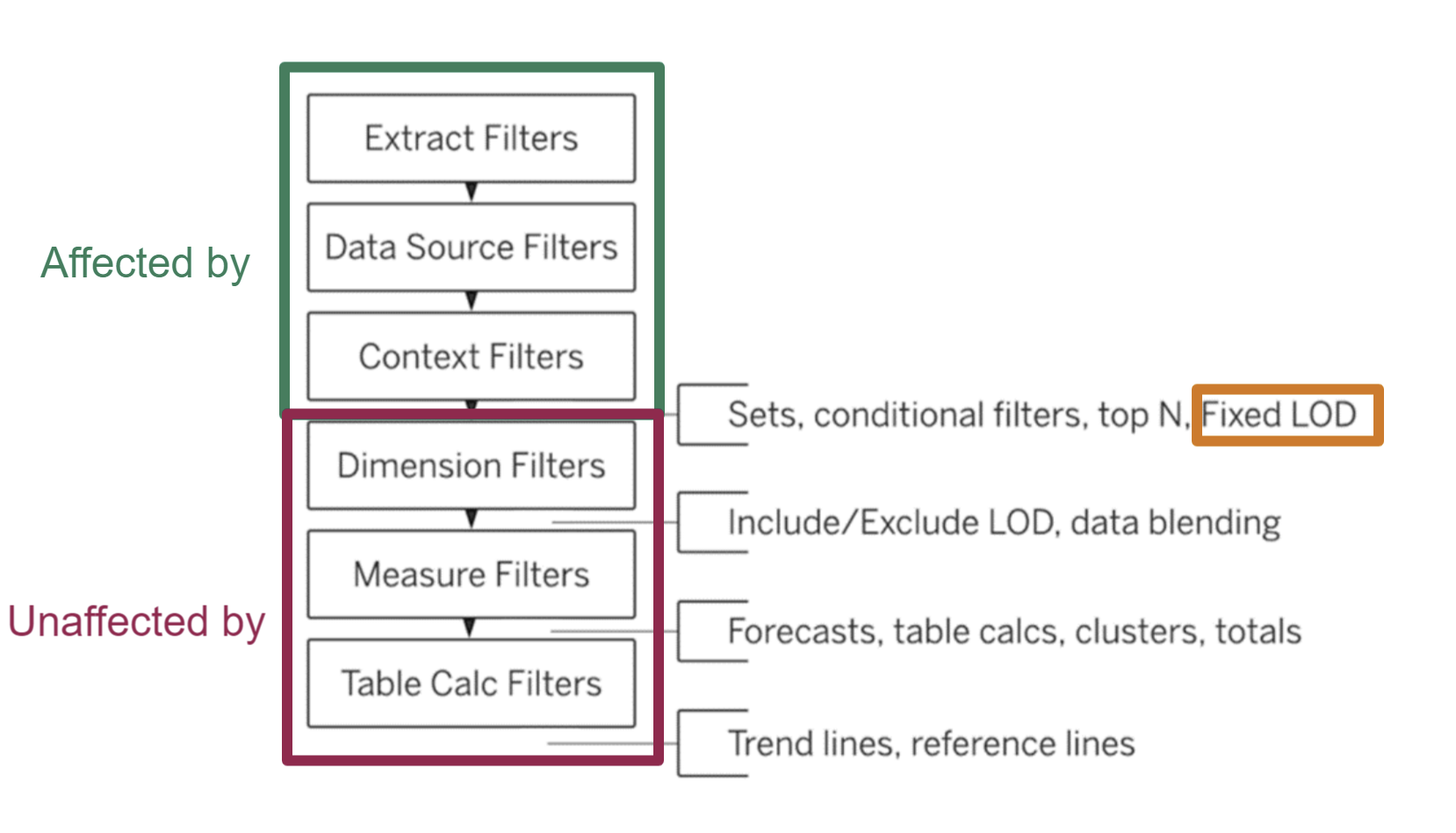
An important thing to note, is that FIXED LOD is not affected by dimension filters, this means that if you but Sub-category on filters the FIXED calculation will remain the same unless you add the Sub-category to context.
EXCLUDE LOD
Unlike FIXED LOD, EXCLUDE LOD acknowledges everything in the view, so the dimension in the expression tells it what to ignore. EXCLUDE makes it less granular.
Example:
Below is saying ignore Category and Sub-category even though it is in the view and return only Sum of Sales.
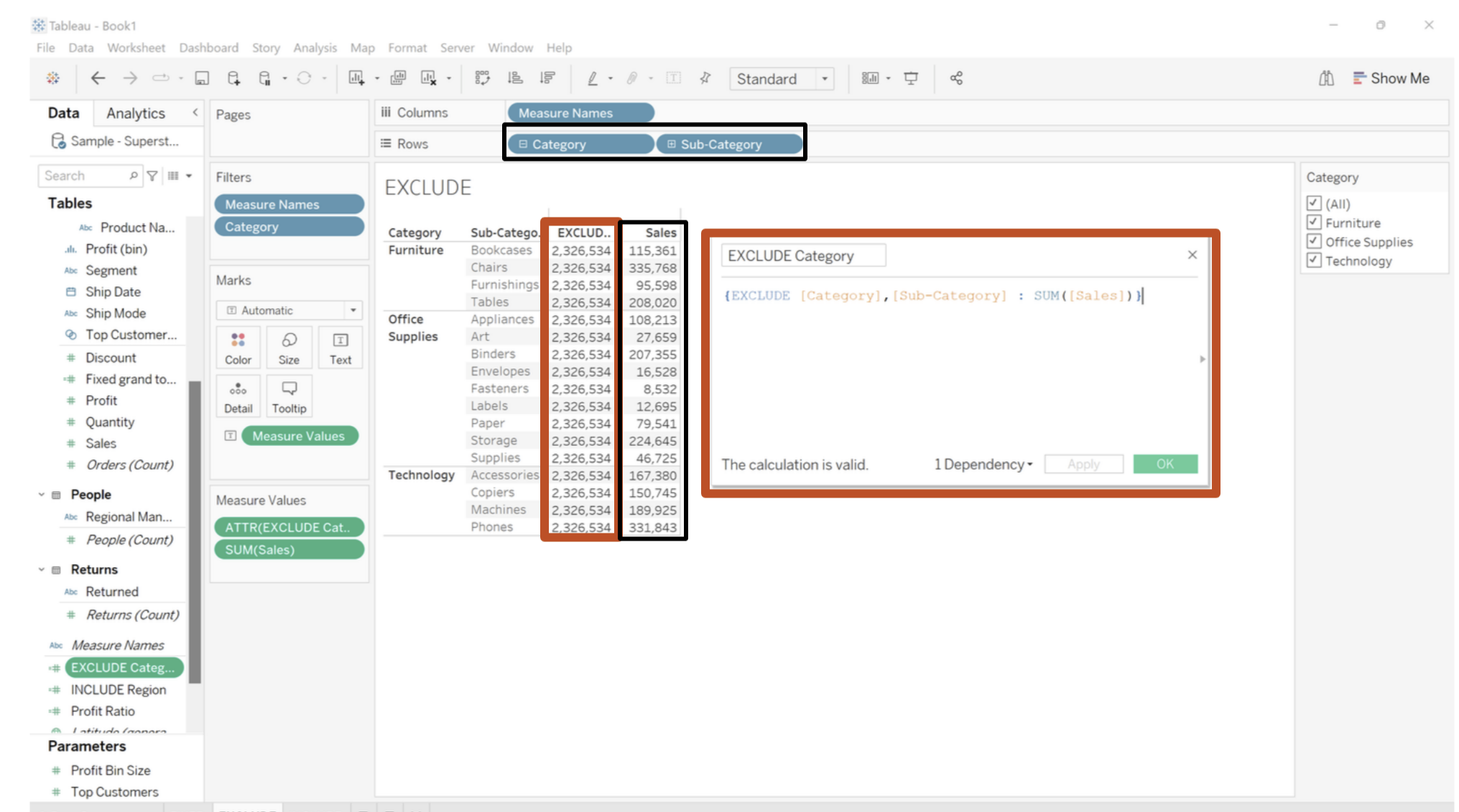
INCLUDE LOD
Unlike EXCLUDE, INCLUDE is more granular as it is adding more detail to what is already in the view. Both INCLUDE & EXCLUSE are affected by dimension filters.
Example:
In the calculation below, we are adding AVG(SUM([Sales])) by customer name to the view through an LOD to show the average customer sales amount by region.

And that is it, all three LODs covered.
