We’ve all found the "perfect" data source, only to realize it's trapped in a web table or spread across hundreds of separate pages. Manual copy pasting is a recipe for errors and a waste of your time.
Web scraping is one way of automating the collection of data from a website. You can "teach" Alteryx to read and extract exactly what you need from a websites raw HTML code. Turning messy data into a clean structured dataset.
In this example, we will be web scraping a website called https://books.toscrape.com. This is a great website to practice web scraping from.
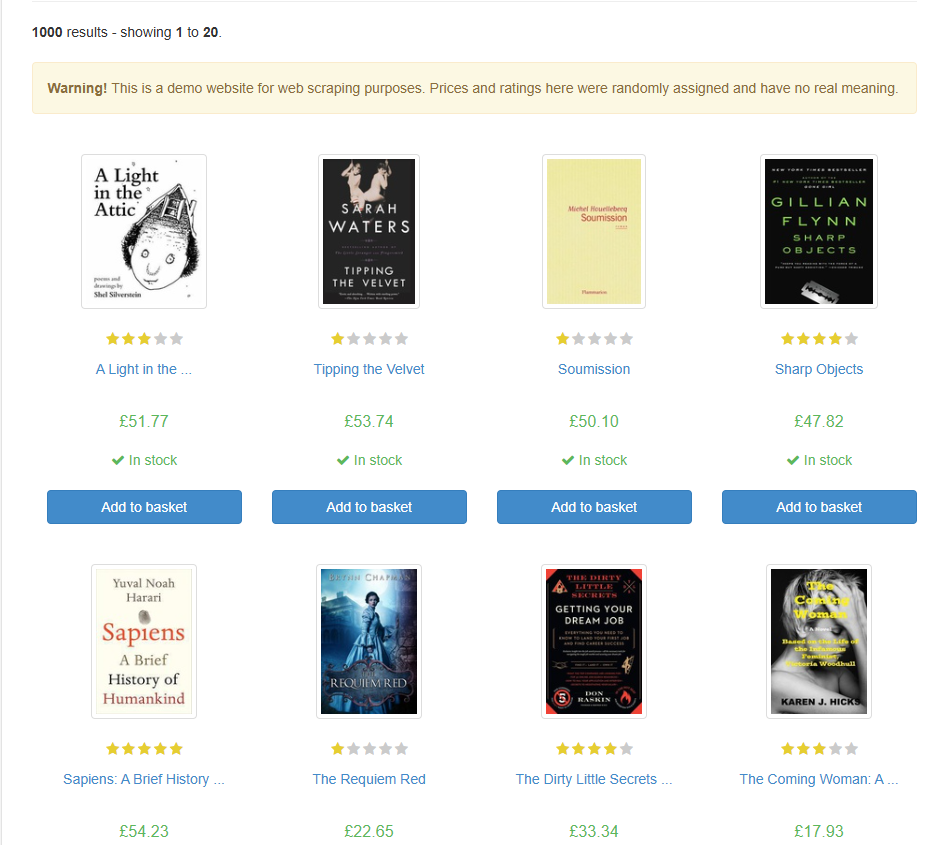
Taking a look at the website we can see that it is listing the books they have for sale.
In this example we will be web scraping this page in order to return:
- The book titles
- The price of the book
- The rating
- If the book is in stock or not
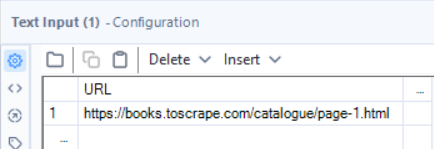
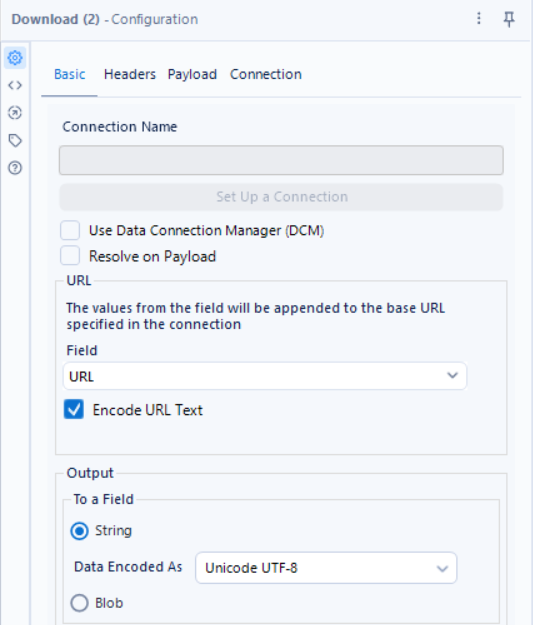
The first step to web scraping is to "download" the data into Alteryx. This is done using a text input tool and a download tool. In the text input tool, paste the URL for the web page you intend on scraping and set up the download tool to download the data from that URL.
Once the HTML has been downloaded into Alteryx, we can start using regex to take out the information that we listed above.
A trick to help find what you are looking for with regex is to right click on the web page you are scraping and select "view page source". This allows you to view the HTML of the webpage. From this you can find where the data you are looking for sits, and therefore what you need to write in the regex tool in order to parse it out.
The Titles:
Looking within the HTML for https://books.toscrape.com, we can see that the titles of the books are available on the line below.

Using the regex tool, we can Tokenize and split to rows every instance of this line appearing in the HTML.

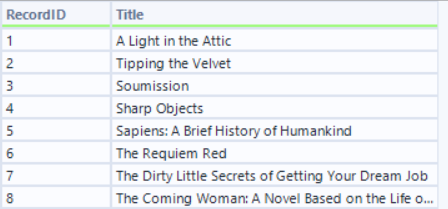
This gives us a field that looks like this
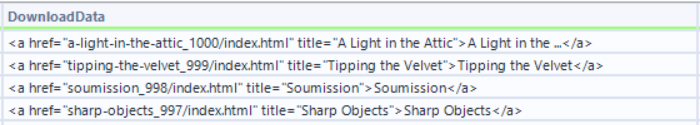
We then need to specifically pull out just the title of the book. Using the regex tool once again, we can parse out just the titles of the books

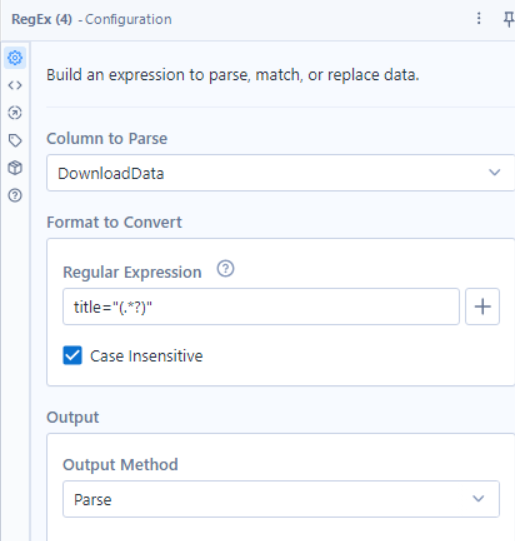
From here, using a select tool, we can remove the fields we no longer require and rename the field for the title.
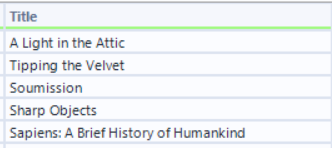
You may have noticed that this has only left us with the titles of the books. In order to extract the other information, we have to create separate branches from the download tool, each parsing out different information and then join them back together using a join multiple tool. In order for each branch to have a common field to join off, we introduce a record ID tool and the end of each branch.
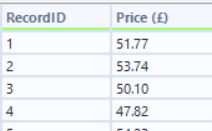
The price:
Extracting the price from the HTML is easier than you would think. Looking at the HTML, we can see that the price value is preceded by the pound sign (£). This allows us to easily use regex to parse the price out.
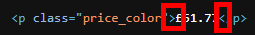
Creating another branch off the download tool, we can add a regex tool and use it to tokenize the prices on to different rows.
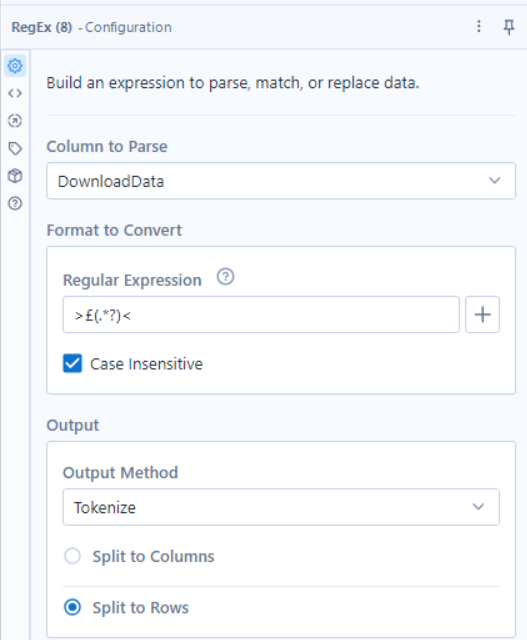
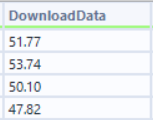
This then leaves us with the raw prices for the books. All that is left to do is to use a select tool to remove the unnecessary fields and to rename the price field and then use the record ID tool to add a record id field.
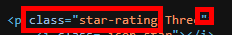
The rating:
Extracting the rating is an identical process to the previous 2. View the page source and find where the data you need is. Then use the regex tool to parse out that data.
Creating another branch from the download tool, we can begin to extract the rating for each book. Looking at the HTML we can see where the rating for each book is located and using the regex tool we can tokenize this to rows in order to get the rating for each book
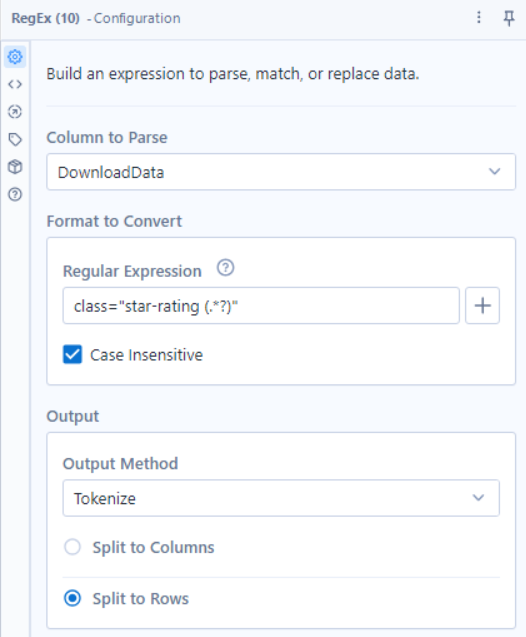
The last step for extracting the ratings is to add a select tool to rename and remove fields, and add a record id using the record ID tool.
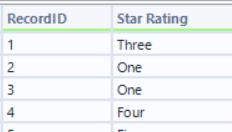
In stock or not:
Finally we are going to be extracting the information for whether the books are in stock or not. This uses the same process as extracting all of the previous information. Looking at the HTML we can see exactly where the information sits.
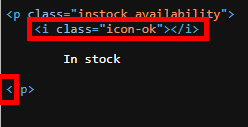
Creating another branch off the download tool, we can use a regex tool to extract the stock data.
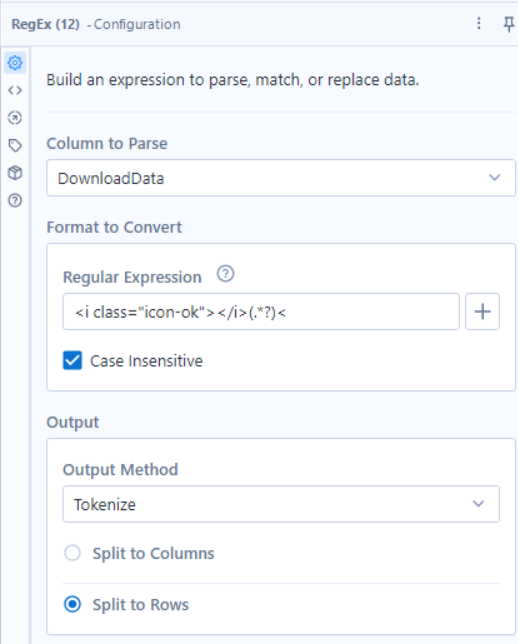
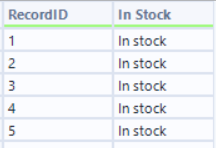
The output of this regex tool will need to be cleaned using a data cleansing tool to remove leading and trailing white space. Then you using a select tool and record ID tool, you can clean your fields reading for joining.
Join multiple:
The final step is to join all of these branches using the join multiple tool on the record ID field.
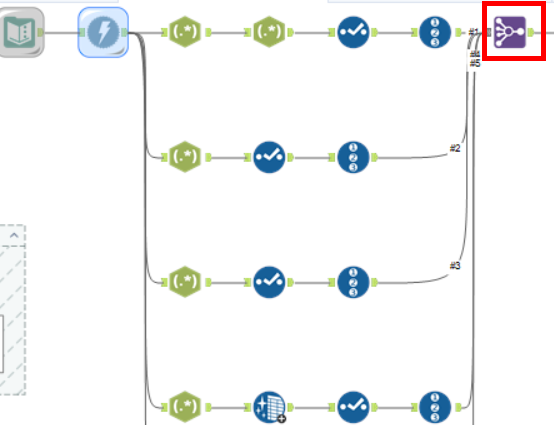
This will then leave you with all of the information about each book on the web page.
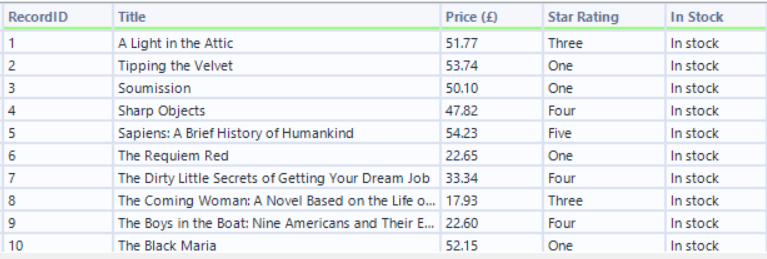
Hopefully this brief guide and follow along has given you some more confidence in how to web scrape using regex in Alteryx.
